Why Abzena?
Trust our focused approach.

ADCs deliver highly potent chemotherapy agents directly to cancer cells via a linker attached to a targeted antibody. Unlock the potential of ADCs with our comprehensive services & solutions. Abzena is a leading partner for Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) development and manufacturing.
We are committed to moving this next generation of medicine forwards. Abzena’s 20+ years of bioconjugation experience and ThioBridge™ ADC design and delivery solution simplifies and accelerates the development process. Our ADC development services provide:

Bioconjugation is an expertise that is essential in the creation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). It facilitates the precise linking of biologically active molecules with potent payloads. At Abzena, we are at the forefront of advanced bioconjugation techniques that enhance the creation of stable and effective ADCs. Utilizing proprietary technologies such as ThioBridge™, we optimize the conjugation process, ensuring the efficacy, safety, and scalability of your therapeutic solutions.
Abzena is committed to supporting every phase of ADC development, from initial discovery to manufacturing, with an emphasis on precision and efficiency.
Download our information sheet titled ‘Streamlining Bioconjugation for Antibody-Drug Conjugate Development’ to learn more.
Developers have long since understood the power of specifically targeting harmful cells and delivering a cytotoxic payload with minimal systemic toxicity – particularly in the treatment of cancer. As a result, ADCs are one of the fastest growing anti-cancer therapeutic areas.
Year of the first ADC approval
ADC drugs approved for marketing worldwide*
Predicted ADC market size in 2030
*As of early 2024.
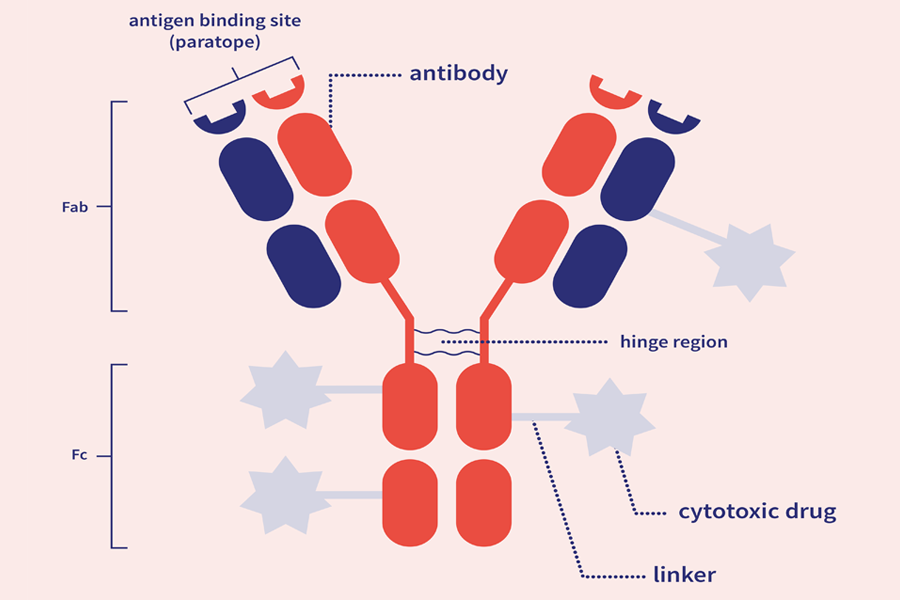
ADCs are comprised of three main components:
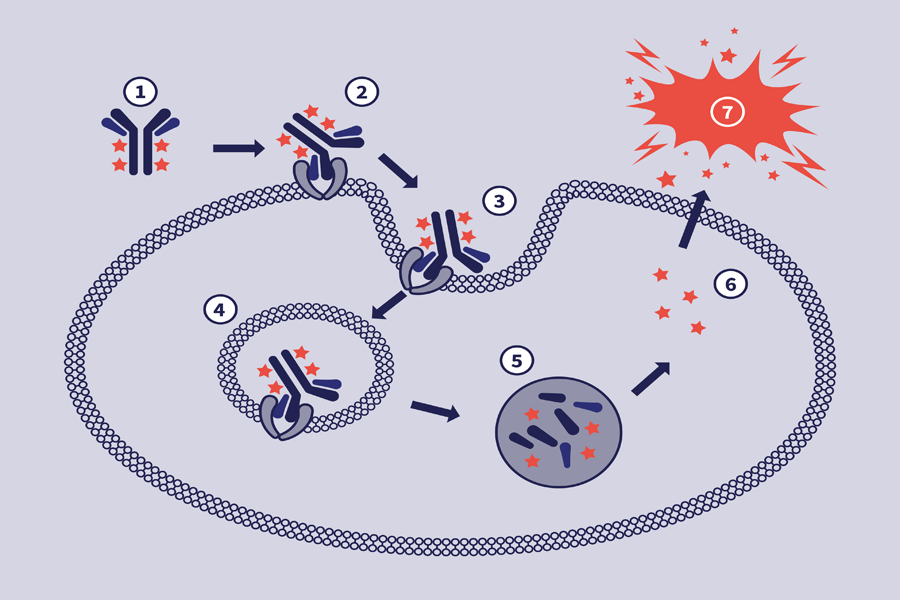
The mechanism of action of ADCs is complex, often requiring internalization, intracellular processing and payload release.
The antibody subunit provides specificity towards cancer cells by recognizing antigens exclusive to, or highly expressed by, cancer cells. Upon recognition, the ADC enters the cell, and the linker is degraded, releasing the cytotoxic.
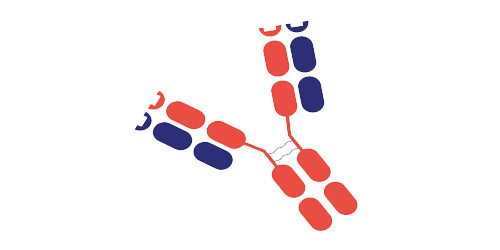
Most cytotoxic drug components are highly potent and belong to two major families: tubulin and DNA-damaging agents. Inappropriate release of these drugs can cause toxic effects, so the drug must remain attached to the antibody until internalization.
The antibody and cytotoxic drug component are generally linked by a covalent linker. Peptide linkers are the most common type, offering stability and the ability to be selectively cleaved by lysosomal proteases following cell uptake.
Development and manufacturing of ADCs is becoming increasingly challenging. For each product, unique hurdles to ADCs must be carefully considered and overcome, and must ensure:
Abzena are experts in developing Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs) through all stages from discovery to commercialization.
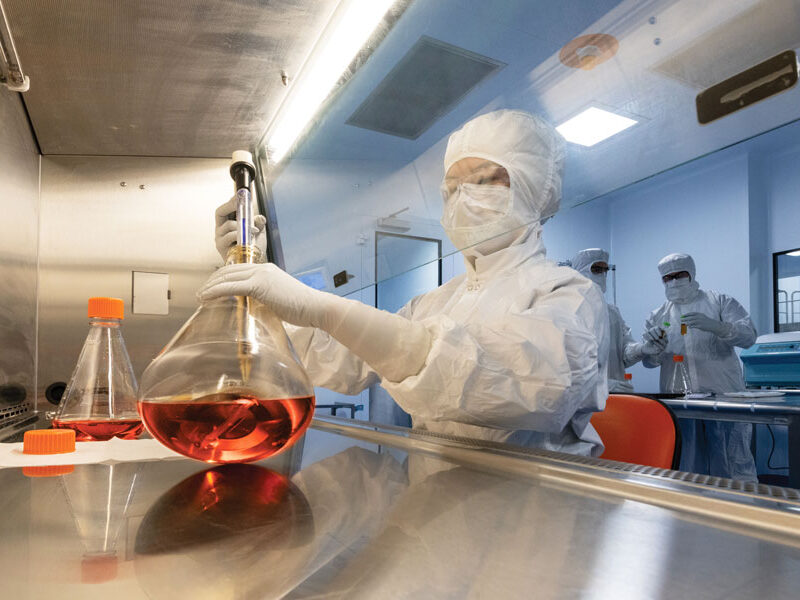

To accelerate lead drug candidate selection, we utilize our expertise in identifying and mapping the appropriate design space for the development of your complex Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs). Through the application of our developability assessments, we identify and de-risk your clinical candidates for development and ensure stage-specific milestones are met.
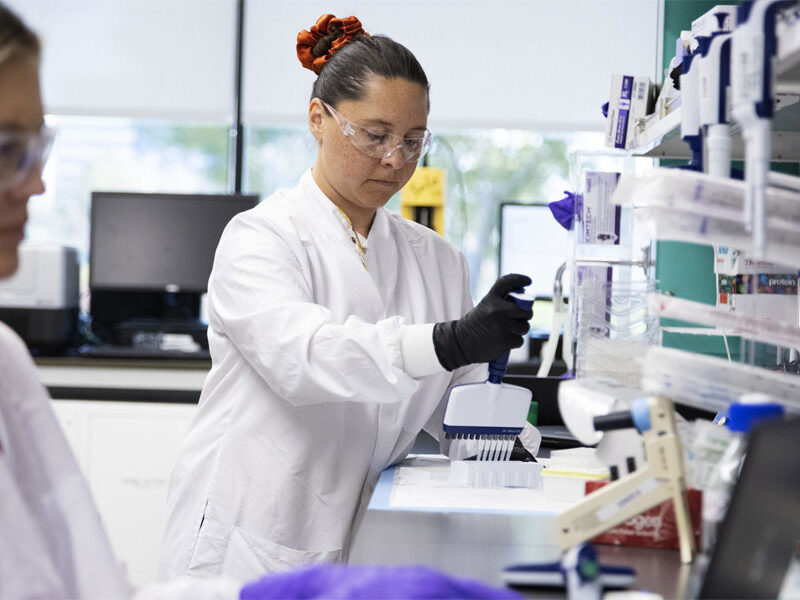

To optimize the design of your molecule, our expert team applies their experience to design the best ADC matrix strategy for you. Your program will benefit from our extensive knowledge of ADCs and bioconjugation. We have experience in the design and development of fully characterized ADCs with a wide range of conventional and novel linkers, cytotoxins, and other payloads. In addition, we provide a range of both proprietary and non-proprietary PEGylation technologies.
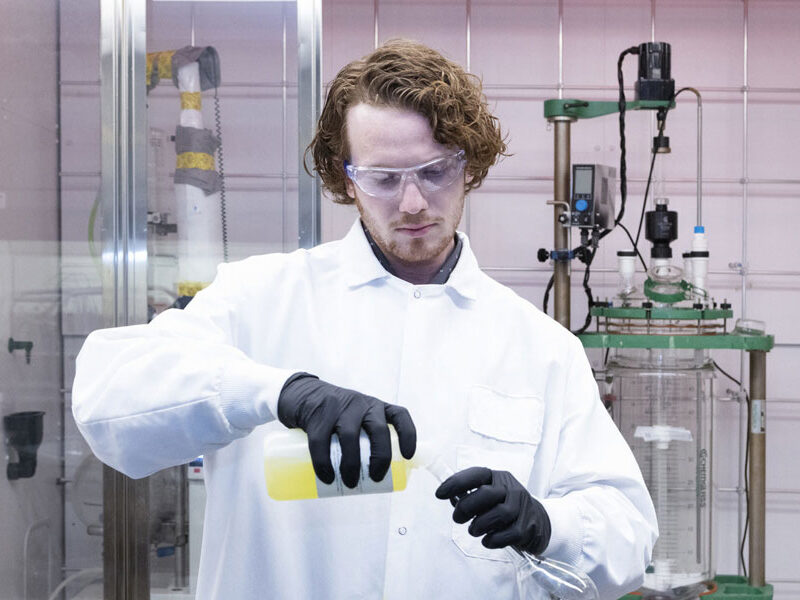

Our experts develop robust conjugation processes maximizing conversion to the target species and purification strategies allowing isolation with high recoveries and purity. Critical process parameters are identified at an early stage to ensure the development of a conjugation process, accelerate your lead candidate, and ensure scale-up of manufacturing.
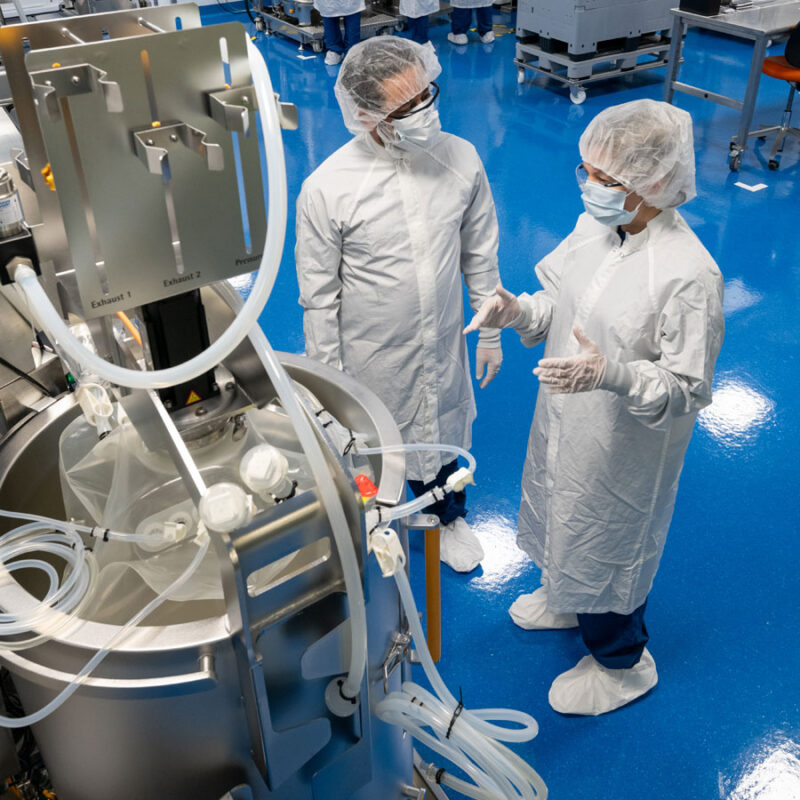

Our unique ThioBridge™ platform is truly next-generation conjugation technology. It overcomes some of the shortcomings of first-generation conjugation technologies, by using site-specific conjugation to antibody interchain disulfide. It offers a more uniform DAR profile and stable attachment compared to maleimide conjugation and allows for PK profiles to be optimized with architectural design flexibility when it comes to the payload and spacer.